FlowLayout Live-Demo: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
K |
K |
||
| (8 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
[[Kategorie:Java-Codeschnipsel]] | [[Kategorie:Java-Codeschnipsel]] | ||
| + | [[Kategorie:LayoutManager]] | ||
| + | '''Autor: Gernot Segieth''' | ||
| + | |||
Die FlowLayout-Live-Demo erleichtert spielerisch durch Erkunden und Verändern von Werten in der Benutzeroberfläche das Verständnis von [[FlowLayout]]. | Die FlowLayout-Live-Demo erleichtert spielerisch durch Erkunden und Verändern von Werten in der Benutzeroberfläche das Verständnis von [[FlowLayout]]. | ||
| Zeile 241: | Zeile 244: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | =Interface FlowOperations - die Funktionen der Demo= | + | =Klassen aus dem Event-Package= |
| + | ==Interface FlowOperations - die Funktionen der Demo== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
package flowlayout.event; | package flowlayout.event; | ||
| Zeile 264: | Zeile 268: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | =AddAction - Hinzufügen neuer Komponenten= | + | ==AddAction - Hinzufügen neuer Komponenten== |
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
package flowlayout.event; | package flowlayout.event; | ||
| Zeile 293: | Zeile 297: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | =RemoveAction - Entfernen von Komponenten= | + | ==RemoveAction - Entfernen von Komponenten== |
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
package flowlayout.event; | package flowlayout.event; | ||
| Zeile 322: | Zeile 326: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | =HgapChangeAction - Horizontalen Abstand einstellen= | + | ==SelectAction - Auswahl in der JComboBox behandeln== |
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | package flowlayout.event; | ||
| + | |||
| + | import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; | ||
| + | import javax.swing.AbstractAction; | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * | ||
| + | * @author Gernot Segieth | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public class SelectAction extends AbstractAction { | ||
| + | |||
| + | private final FlowOperations fo; | ||
| + | |||
| + | public SelectAction(FlowOperations fo) { | ||
| + | this.fo = fo; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) { | ||
| + | fo.changeAlignment(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==HgapChangeAction - Horizontalen Abstand einstellen== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
package flowlayout.event; | package flowlayout.event; | ||
| Zeile 348: | Zeile 379: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | =VgapChangeAction - Vertikalen Abstand einstellen= | + | ==VgapChangeAction - Vertikalen Abstand einstellen== |
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
package flowlayout.event; | package flowlayout.event; | ||
| Zeile 372: | Zeile 403: | ||
} | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Ein Renderer für die JComboBox= | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | package flowlayout; | ||
| + | |||
| + | import java.awt.Component; | ||
| + | import java.awt.FlowLayout; | ||
| + | import javax.swing.DefaultListCellRenderer; | ||
| + | import javax.swing.JList; | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * | ||
| + | * @author Gernot Segieth | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | public class AlignmentComboBoxRenderer extends DefaultListCellRenderer { | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public Component getListCellRendererComponent(JList<?> list, Object value, int index, boolean isSelected, boolean cellHasFocus) { | ||
| + | super.getListCellRendererComponent(list, value, index, isSelected, cellHasFocus); | ||
| + | if (value instanceof Integer) { | ||
| + | Integer intValue = (Integer) value; | ||
| + | switch (intValue) { | ||
| + | case FlowLayout.LEADING: | ||
| + | this.setText("LEADING"); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case FlowLayout.LEFT: | ||
| + | this.setText("LEFT"); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case FlowLayout.RIGHT: | ||
| + | this.setText("RIGHT"); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | case FlowLayout.TRAILING: | ||
| + | this.setText("TRAILING"); | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | default: | ||
| + | this.setText("CENTER"); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | return this; | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Icons= | ||
| + | Fehlen nur noch die Icons, die auch als Java-Klasse angelegt werden können. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zunächst das Minus-Icon: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | package flowlayout.icons; | ||
| + | |||
| + | import java.awt.BasicStroke; | ||
| + | import java.awt.Component; | ||
| + | import java.awt.Graphics; | ||
| + | import java.awt.Graphics2D; | ||
| + | import java.awt.Shape; | ||
| + | import java.awt.geom.AffineTransform; | ||
| + | import java.awt.geom.GeneralPath; | ||
| + | import java.awt.geom.Path2D; | ||
| + | import javax.swing.Icon; | ||
| + | |||
| + | public class LessIcon implements Icon { | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics gr, int x, int y) { | ||
| + | Graphics2D g = (Graphics2D) gr; | ||
| + | AffineTransform at = new AffineTransform(); | ||
| + | at.translate(x, y); | ||
| + | at.scale(getIconWidth(), getIconHeight()); | ||
| + | Shape transformedShape = at.createTransformedShape(createShape()); | ||
| + | g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2)); | ||
| + | g.draw(transformedShape); | ||
| + | g.dispose(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public int getIconWidth() { | ||
| + | return 15; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public int getIconHeight() { | ||
| + | return getIconWidth(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | private Shape createShape() { | ||
| + | Path2D path = new GeneralPath(); | ||
| + | path.moveTo(0.1f, 0.5f); | ||
| + | path.lineTo(0.9f, 0.5f); | ||
| + | return path; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Das Plus-Icon: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | package flowlayout.icons; | ||
| + | |||
| + | import java.awt.BasicStroke; | ||
| + | import java.awt.Component; | ||
| + | import java.awt.Graphics; | ||
| + | import java.awt.Graphics2D; | ||
| + | import java.awt.Shape; | ||
| + | import java.awt.geom.AffineTransform; | ||
| + | import java.awt.geom.GeneralPath; | ||
| + | import java.awt.geom.Path2D; | ||
| + | import javax.swing.Icon; | ||
| + | |||
| + | public class MoreIcon implements Icon { | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics gr, int x, int y) { | ||
| + | Graphics2D g = (Graphics2D) gr; | ||
| + | AffineTransform at = new AffineTransform(); | ||
| + | at.translate(x, y); | ||
| + | at.scale(getIconWidth(), getIconHeight()); | ||
| + | Shape transformedShape = at.createTransformedShape(createShape()); | ||
| + | g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2)); | ||
| + | g.draw(transformedShape); | ||
| + | g.dispose(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public int getIconWidth() { | ||
| + | return 15; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public int getIconHeight() { | ||
| + | return getIconWidth(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | private Shape createShape() { | ||
| + | Path2D path = new GeneralPath(); | ||
| + | path.moveTo(0.5f, 0.1f); | ||
| + | path.lineTo(0.5f, 0.9f); | ||
| + | path.moveTo(0.1f, 0.5f); | ||
| + | path.lineTo(0.9f, 0.5f); | ||
| + | return path; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
{{Fragen stellen}} | {{Fragen stellen}} | ||
| − | Mehr zum [[FlowLayout]] und anderen [[LayoutManager der Standard-Java-API|LayoutManagern]] | + | =Weiterführende Links= |
| + | *Mehr zum [[FlowLayout]] und anderen [[LayoutManager der Standard-Java-API|LayoutManagern]] | ||
| + | *[[JSpinner mit Zahl und Einheit]] | ||
| + | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 14. November 2021, 17:15 Uhr
Autor: Gernot Segieth
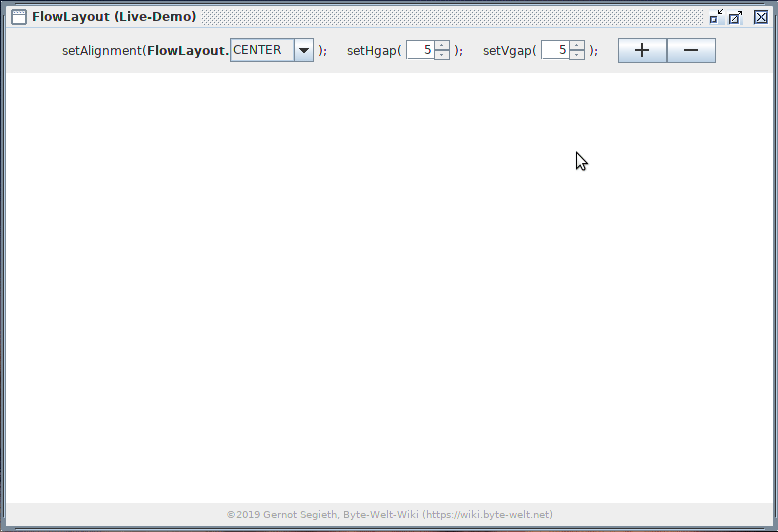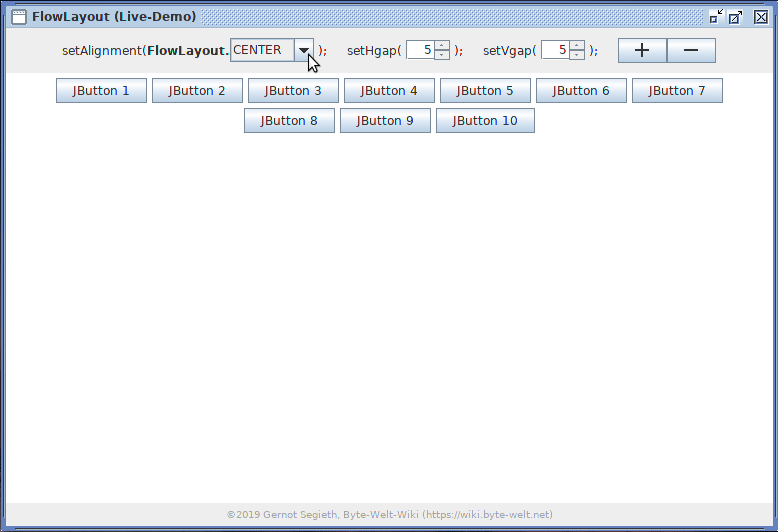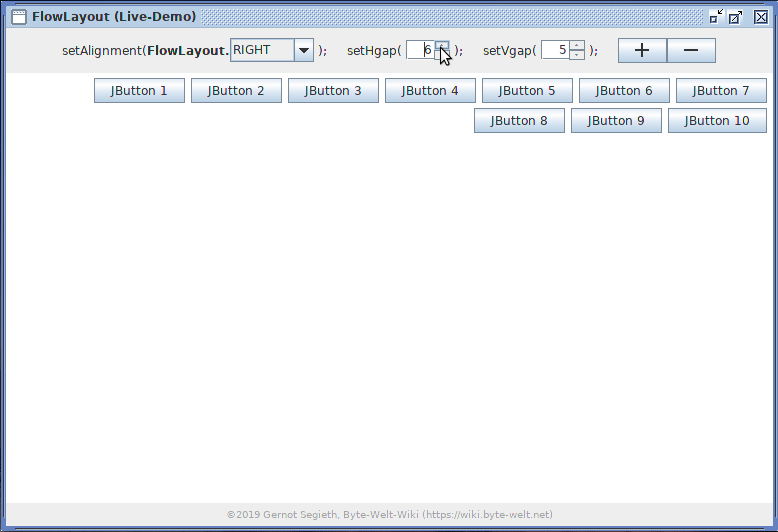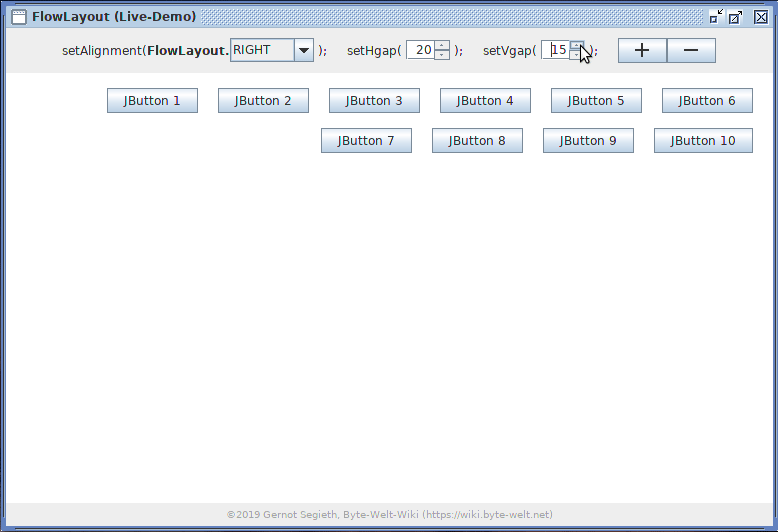
Die FlowLayout-Live-Demo erleichtert spielerisch durch Erkunden und Verändern von Werten in der Benutzeroberfläche das Verständnis von FlowLayout.
Kopieren Sie sich die Quellcodes in einzelne Java-Dateien. Achten Sie auf die richtige Verteilung der Klassen in die im Code angegebenen Packages, oder kommentieren Sie die Package-Anweisung einfach aus, wenn Sie unsicher sind. Anschließend kompilieren Sie die Java-Dateien und starten die Hauptklasse.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 FlowLayoutDemo.java - Die Hauptklasse
- 2 Klassen aus dem Event-Package
- 2.1 Interface FlowOperations - die Funktionen der Demo
- 2.2 AddAction - Hinzufügen neuer Komponenten
- 2.3 RemoveAction - Entfernen von Komponenten
- 2.4 SelectAction - Auswahl in der JComboBox behandeln
- 2.5 HgapChangeAction - Horizontalen Abstand einstellen
- 2.6 VgapChangeAction - Vertikalen Abstand einstellen
- 3 Ein Renderer für die JComboBox
- 4 Icons
- 5 Fragen
- 6 Weiterführende Links
FlowLayoutDemo.java - Die Hauptklasse
/*
* FlowLayout-Live-Demo
*
* Copyright (c) 2019 Gernot Segieth - wiki.byte-welt.net
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person
* obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation
* files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without
* restriction, including without limitation the rights to use,
* copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the
* Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following
* conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be
* included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
* EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES
* OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
* NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT
* HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
* WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING
* FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR
* OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
*/
package flowlayout;
import flowlayout.event.AddAction;
import flowlayout.event.FlowOperations;
import flowlayout.event.HgapChangeAction;
import flowlayout.event.RemoveAction;
import flowlayout.event.SelectAction;
import flowlayout.event.VgapChangeAction;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.GridBagConstraints;
import java.awt.GridBagLayout;
import java.awt.Insets;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import javax.swing.BorderFactory;
import javax.swing.ComboBoxModel;
import javax.swing.DefaultComboBoxModel;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JSpinner;
import javax.swing.SpinnerNumberModel;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
/**
* Die FlowLayout-Live-Demo erleichtert spielerisch durch Erkunden und Verändern
* von Werten in der Benutzeroberfläche das Verständnis von FlowLayout.
*
* @author Gernot Segieth, (c)2019
* @see java.awt.FlowLayout
*/
public class FlowLayoutDemo implements FlowOperations {
private JPanel flowPanel;
private FlowLayout layout;
private SpinnerNumberModel hgapModel; //JSpinner zur Eingabe horizontaler Abstände
private SpinnerNumberModel vgapModel; //JSpinner zur Eingabe vertikaler Abstände
private ComboBoxModel<Integer> alignArgumentModel;
private int compCount; //zählt die Komponenten
public FlowLayoutDemo() {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("FlowLayout (Live-Demo)");
frame.add(createFlowPanel(), BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.add(createControlPanel(), BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(createSouthPanel(), BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.pack();
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
@Override
public void addComponent() {
flowPanel.add(new JButton("JButton " + (++compCount)));
flowPanel.validate();
flowPanel.repaint();
}
@Override
public void removeComponent() {
if (compCount > 0) {
flowPanel.remove(--compCount);
flowPanel.validate();
flowPanel.repaint();
}
}
@Override
public void changeAlignment() {
int alignment = (Integer) alignArgumentModel.getSelectedItem();
layout.setAlignment(alignment);
update();
}
@Override
public void changeHgap() {
layout.setHgap((int) hgapModel.getNumber());
update();
}
@Override
public void changeVgap() {
layout.setVgap((int) vgapModel.getNumber());
update();
}
private JPanel createFlowPanel() {
layout = new FlowLayout();
flowPanel = new JPanel(layout) {
@Override
public Dimension getPreferredSize() {
Dimension size = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getScreenSize();
return new Dimension(size.width * 40 / 100, size.height * 40 / 100);
}
};
flowPanel.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
return flowPanel;
}
private JPanel createControlPanel() {
JButton addButton = new JButton(new AddAction(this));
JButton removeButton = new JButton(new RemoveAction(this));
alignArgumentModel = createComboBoxModel();
JComboBox<Integer> alignBox = new JComboBox<>(alignArgumentModel);
alignBox.setEditable(false);
alignBox.setRenderer(new AlignmentComboBoxRenderer());
alignBox.addActionListener(new SelectAction(this));
hgapModel = new SpinnerNumberModel(layout.getHgap(), 0, 50, 1);
JSpinner hgapSpinner = new JSpinner(hgapModel);
hgapSpinner.addChangeListener(new HgapChangeAction(this));
vgapModel = new SpinnerNumberModel(layout.getVgap(), 0, 50, 1);
JSpinner vgapSpinner = new JSpinner(vgapModel);
vgapSpinner.addChangeListener(new VgapChangeAction(this));
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
panel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(10, 0, 10, 0));
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
int space = 20;
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 0;
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(new JLabel("<html>setAlignment(<strong>FlowLayout.</strong></html> "), gbc);
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(alignBox, gbc);
gbc.insets = new Insets(0, 0, 0, space);
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(new JLabel(" );"), gbc);
gbc.insets = new Insets(0, 0, 0, 0);
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(new JLabel("setHgap( "), gbc);
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(hgapSpinner, gbc);
gbc.insets = new Insets(0, 0, 0, space);
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(new JLabel(" );"), gbc);
gbc.insets = new Insets(0, 0, 0, 0);
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(new JLabel("setVgap( "), gbc);
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(vgapSpinner, gbc);
gbc.insets = new Insets(0, 0, 0, space);
gbc.gridx++;
panel.add(new JLabel(" );"), gbc);
panel.add(addButton);
panel.add(removeButton);
return panel;
}
private JPanel createSouthPanel() {
JLabel label = new JLabel("<html>©2019 Gernot Segieth, Byte-Welt-Wiki (https://wiki.byte-welt.net)</html>");
label.setForeground(label.getBackground().darker());
label.setFont(label.getFont().deriveFont(10f));
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
panel.add(label);
return panel;
}
private ComboBoxModel<Integer> createComboBoxModel() {
Integer[] items = new Integer[]{
FlowLayout.CENTER,
FlowLayout.LEADING,
FlowLayout.LEFT,
FlowLayout.RIGHT,
FlowLayout.TRAILING
};
alignArgumentModel = new DefaultComboBoxModel<>(items);
alignArgumentModel.setSelectedItem(layout.getAlignment());
return alignArgumentModel;
}
private void update() {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
flowPanel.updateUI();
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame.setDefaultLookAndFeelDecorated(true);
UIManager.put("swing.boldMetal", false);
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
new FlowLayoutDemo();
});
}
}
Klassen aus dem Event-Package
Interface FlowOperations - die Funktionen der Demo
package flowlayout.event;
/**
*
* @author Gernot Segieth
*/
public interface FlowOperations {
public void addComponent();
public void removeComponent();
public void changeAlignment();
public void changeHgap();
public void changeVgap();
}
AddAction - Hinzufügen neuer Komponenten
package flowlayout.event;
import gridlayout.icons.MoreIcon;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import javax.swing.AbstractAction;
/**
*
* @author Gernot Segieth
*/
public class AddAction extends AbstractAction {
private final FlowOperations fo;
public AddAction(FlowOperations fo) {
super("", new MoreIcon());
this.fo = fo;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) {
fo.addComponent();
}
}
RemoveAction - Entfernen von Komponenten
package flowlayout.event;
import gridlayout.icons.LessIcon;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import javax.swing.AbstractAction;
/**
*
* @author Gernot Segieth
*/
public class RemoveAction extends AbstractAction {
private final FlowOperations fo;
public RemoveAction(FlowOperations fo) {
super("", new LessIcon());
this.fo = fo;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) {
fo.removeComponent();
}
}
SelectAction - Auswahl in der JComboBox behandeln
package flowlayout.event;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import javax.swing.AbstractAction;
/**
*
* @author Gernot Segieth
*/
public class SelectAction extends AbstractAction {
private final FlowOperations fo;
public SelectAction(FlowOperations fo) {
this.fo = fo;
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) {
fo.changeAlignment();
}
}
HgapChangeAction - Horizontalen Abstand einstellen
package flowlayout.event;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeEvent;
/**
*
* @author Gernot Segieth
*/
public class HgapChangeAction extends AbstractChangeAction {
private FlowOperations fo;
public HgapChangeAction(FlowOperations fo) {
this.fo = fo;
}
@Override
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent ce) {
fo.changeHgap();
}
}
VgapChangeAction - Vertikalen Abstand einstellen
package flowlayout.event;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeEvent;
/**
*
* @author Gernot Segieth
*/
public class VgapChangeAction extends AbstractChangeAction {
private FlowOperations fo;
public VgapChangeAction(FlowOperations fo) {
this.fo = fo;
}
@Override
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent ce) {
fo.changeVgap();
}
}
Ein Renderer für die JComboBox
package flowlayout;
import java.awt.Component;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.DefaultListCellRenderer;
import javax.swing.JList;
/**
*
* @author Gernot Segieth
*/
public class AlignmentComboBoxRenderer extends DefaultListCellRenderer {
@Override
public Component getListCellRendererComponent(JList<?> list, Object value, int index, boolean isSelected, boolean cellHasFocus) {
super.getListCellRendererComponent(list, value, index, isSelected, cellHasFocus);
if (value instanceof Integer) {
Integer intValue = (Integer) value;
switch (intValue) {
case FlowLayout.LEADING:
this.setText("LEADING");
break;
case FlowLayout.LEFT:
this.setText("LEFT");
break;
case FlowLayout.RIGHT:
this.setText("RIGHT");
break;
case FlowLayout.TRAILING:
this.setText("TRAILING");
break;
default:
this.setText("CENTER");
}
}
return this;
}
}
Icons
Fehlen nur noch die Icons, die auch als Java-Klasse angelegt werden können.
Zunächst das Minus-Icon:
package flowlayout.icons;
import java.awt.BasicStroke;
import java.awt.Component;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.Shape;
import java.awt.geom.AffineTransform;
import java.awt.geom.GeneralPath;
import java.awt.geom.Path2D;
import javax.swing.Icon;
public class LessIcon implements Icon {
@Override
public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics gr, int x, int y) {
Graphics2D g = (Graphics2D) gr;
AffineTransform at = new AffineTransform();
at.translate(x, y);
at.scale(getIconWidth(), getIconHeight());
Shape transformedShape = at.createTransformedShape(createShape());
g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
g.draw(transformedShape);
g.dispose();
}
@Override
public int getIconWidth() {
return 15;
}
@Override
public int getIconHeight() {
return getIconWidth();
}
private Shape createShape() {
Path2D path = new GeneralPath();
path.moveTo(0.1f, 0.5f);
path.lineTo(0.9f, 0.5f);
return path;
}
}
Das Plus-Icon:
package flowlayout.icons;
import java.awt.BasicStroke;
import java.awt.Component;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.Shape;
import java.awt.geom.AffineTransform;
import java.awt.geom.GeneralPath;
import java.awt.geom.Path2D;
import javax.swing.Icon;
public class MoreIcon implements Icon {
@Override
public void paintIcon(Component c, Graphics gr, int x, int y) {
Graphics2D g = (Graphics2D) gr;
AffineTransform at = new AffineTransform();
at.translate(x, y);
at.scale(getIconWidth(), getIconHeight());
Shape transformedShape = at.createTransformedShape(createShape());
g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
g.draw(transformedShape);
g.dispose();
}
@Override
public int getIconWidth() {
return 15;
}
@Override
public int getIconHeight() {
return getIconWidth();
}
private Shape createShape() {
Path2D path = new GeneralPath();
path.moveTo(0.5f, 0.1f);
path.lineTo(0.5f, 0.9f);
path.moveTo(0.1f, 0.5f);
path.lineTo(0.9f, 0.5f);
return path;
}
}
Fragen
Das Thema wurde nicht ausreichend behandelt? Du hast Fragen dazu und brauchst weitere Informationen? Lass Dir von uns helfen!
- Besuche uns im Byte-Welt-Forum
- Besuche unseren Chat
Wir helfen dir gerne!
Dir hat dieser Artikel gefallen? Oder Du hast Fehler entdeckt und möchtest zur Berichtigung beitragen? Prima! Schreibe einen Kommentar!
Du musst angemeldet sein, um einen Kommentar abzugeben.
Weiterführende Links
- Mehr zum FlowLayout und anderen LayoutManagern
- JSpinner mit Zahl und Einheit